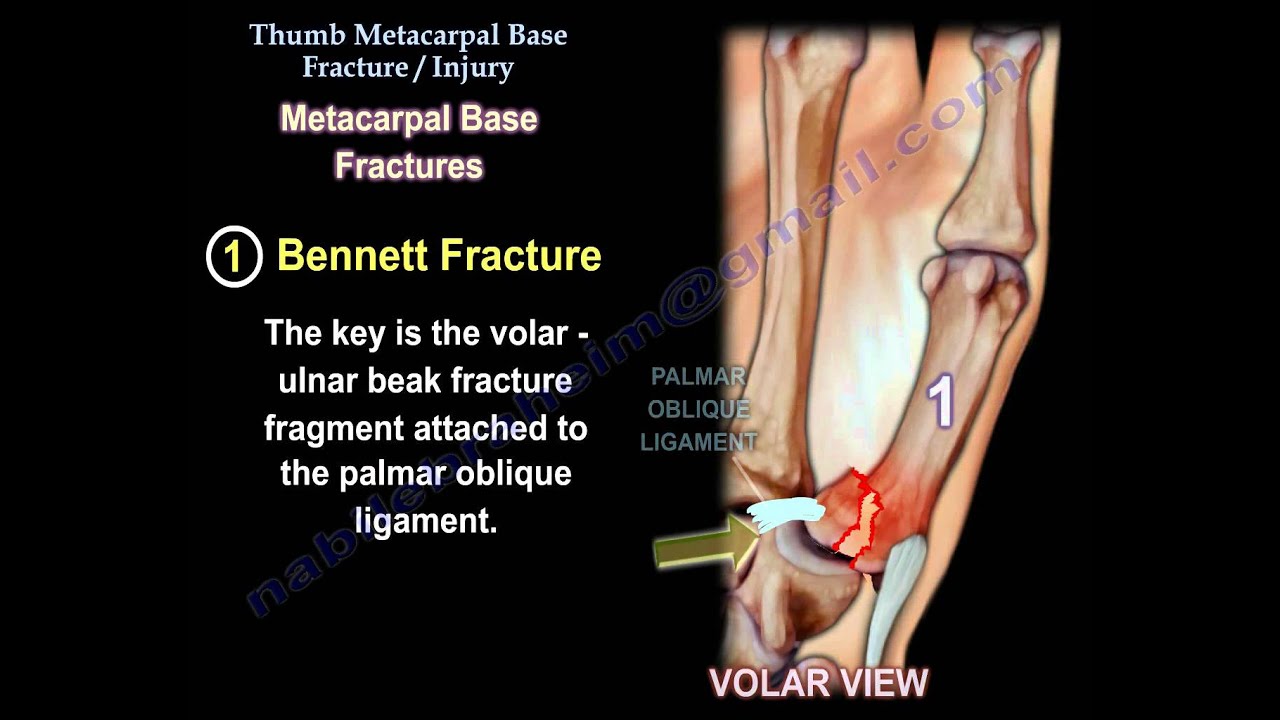
Understanding CMC Injury: Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment
CMC injury, or carpometacarpal injury, is a common medical condition that affects the joints of the hand, particularly at the base of the thumb. This type of injury can lead to significant pain and dysfunction, impacting daily activities and quality of life. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of CMC injuries, including their causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention strategies. Understanding CMC injury is essential for effective management and recovery, whether you are an athlete, a manual laborer, or someone who engages in everyday hand-intensive tasks.
Carpometacarpal injuries can result from a variety of factors, including trauma, repetitive strain, and degenerative conditions. Recognizing the symptoms early can help prevent complications and facilitate timely treatment. We will delve into the anatomy of the CMC joint, the common causes of injury, and the latest treatment methods to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of this condition.
Whether you are experiencing symptoms yourself or are interested in learning more for educational purposes, this article is designed to equip you with the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of CMC injury. Get ready to explore a detailed examination of this topic that affects many individuals worldwide.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the CMC Joint
- Causes of CMC Injury
- Symptoms of CMC Injury
- Diagnosis of CMC Injury
- Treatment Options for CMC Injury
- Rehabilitation and Recovery
- Preventing CMC Injury
- When to See a Doctor
Understanding the CMC Joint
The carpometacarpal (CMC) joint is located at the base of the thumb and is critical for hand function. It allows for a wide range of movements, including grasping, pinching, and rotating.
Anatomy of the CMC Joint
The CMC joint consists of the carpal bones and the metacarpal bone of the thumb. It is a saddle joint, which allows for greater flexibility and movement compared to other types of joints. The ligaments surrounding the joint provide stability, while the tendons allow for muscle movement.
Importance of the CMC Joint
- Enables thumb opposition, crucial for grip strength.
- Facilitates fine motor skills necessary for daily tasks.
- Supports overall hand function and dexterity.
Causes of CMC Injury
CMC injuries can arise from various causes, including:
- Trauma: Direct impact or fall that affects the thumb joint.
- Repetitive Strain: Activities that require repetitive thumb motion, such as typing or manual labor.
- Degenerative Conditions: Arthritis or other degenerative diseases that weaken the joint over time.
- Genetic Predisposition: Some individuals may be more prone to CMC injuries due to inherited joint conditions.
Symptoms of CMC Injury
Recognizing the symptoms of CMC injury is crucial for timely intervention. Common symptoms include:
- Pain at the base of the thumb, especially during movement.
- Swelling or inflammation around the joint.
- Decreased range of motion in the thumb.
- Difficulty gripping or pinching objects.
- Grinding sensation when moving the thumb.
Diagnosis of CMC Injury
Diagnosing a CMC injury typically involves the following steps:
- Medical History: Discussing symptoms and any prior injuries with a healthcare provider.
- Physical Examination: Assessing the thumb's range of motion, strength, and pain levels.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays or MRI scans may be used to evaluate the extent of the injury.
Treatment Options for CMC Injury
Treatment for CMC injury varies depending on the severity of the condition:
Conservative Treatment
- Rest: Avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms.
- Ice Therapy: Applying ice packs to reduce swelling.
- Medication: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to alleviate pain.
- Bracing: Using a splint to immobilize the joint during healing.
Advanced Treatment
- Corticosteroid Injections: To reduce inflammation and pain.
- Physical Therapy: Strengthening exercises to improve function.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgical intervention may be required to repair or reconstruct the joint.
Rehabilitation and Recovery
Recovering from a CMC injury often involves a structured rehabilitation program:
- Initial Phase: Focus on reducing pain and inflammation.
- Strengthening Phase: Gradually introducing exercises to restore strength.
- Functional Phase: Engaging in activities that mimic daily tasks to ensure full recovery.
Preventing CMC Injury
Preventing CMC injuries is key to maintaining thumb health:
- Ergonomic Tools: Use tools designed to minimize strain on the hands.
- Stretching: Incorporate hand and thumb stretches into your routine.
- Strength Training: Perform exercises that target hand and thumb strength.
When to See a Doctor
It is essential to seek medical attention if you experience:
- Persistent pain that does not improve with home care.
- Significant swelling or bruising.
- Inability to move the thumb or perform daily tasks.
Conclusion
CMC injury can significantly impact hand function and quality of life, but understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatments can help manage this condition effectively. If you suspect you have a CMC injury, it is crucial to seek medical evaluation and adhere to recommended treatment plans. Remember, early intervention can lead to better outcomes and a quicker return to daily activities.
We encourage you to leave a comment below, share this article with others who may find it helpful, or explore more of our content on hand health and injury prevention.
Final Thoughts
Thank you for reading about CMC injury. We hope this information has been valuable to you. Be sure to visit our site again for more insightful articles on health and wellness.
Next Fed's Meeting: Insights And Expectations
Jack Reacher Season 2: Everything You Need To Know
Ultimate Guide To Play Spades: Master The Game Like A Pro